Cannabis And CO2: Why Plants Suffer If They Don’t Get At Least A Minimum Amount Of CO2
Indoor Co2 tank.
Healthy plants need a supply of carbon dioxide (CO2) just as they need nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, or any other required nutrient. The carbon dioxide content of fresh outdoor air comprises about 406 parts per million (ppm) of the earth’s atmosphere. It is critical for photosynthesis and cannabis plants suffer if they don’t get at least a minimum amount of CO2.
how cannabis uses CO2
Cannabis uses CO2 in the presence of light. Photosynthesis occurs when the plant receives light. The marijuana plant draws in CO2 from the air by tiny openings on the undersides of leaves called stomata. They function much like pores in the skin, but have guard cells that can open and close. They regulate the absorption of water, gas, oxygen, (O2), and CO2 into the plant, as well as the evacuation of water and O2 from the plant.
It is critical for photosynthesis and cannabis plants suffer if they don’t get at least a minimum amount of CO2.
Once CO2 is absorbed into the plant, it is directed to the chloroplasts—the plant organelles that contain light-absorbing chlorophylls—where photosynthesis takes place.
Photosynthesis consists of a complex series of reactions in which light energy is used to convert carbon dioxide and water to sugar, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
photosynthesis and plant growth
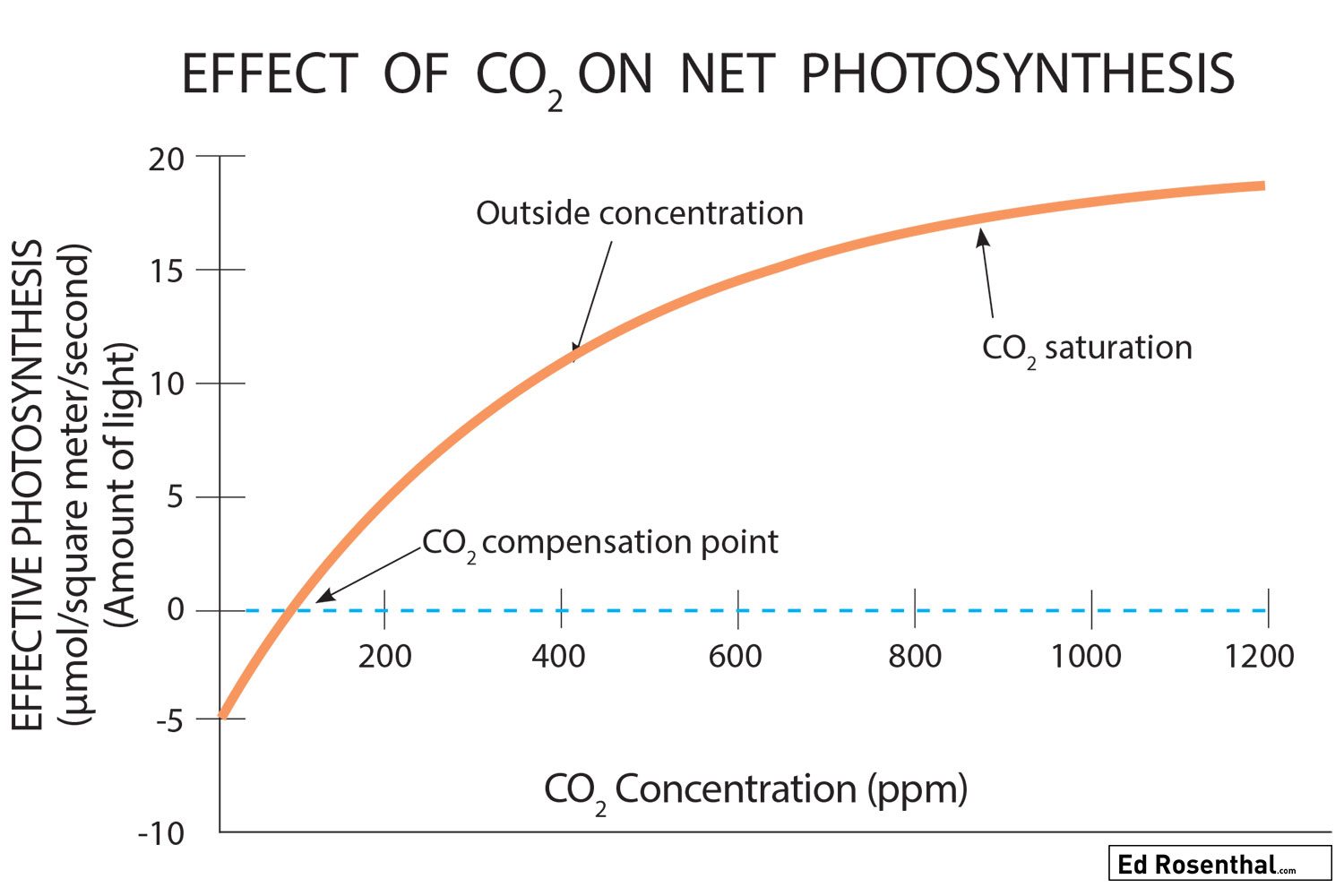
The amount of CO2 in the air has a profound effect on the rate of photosynthesis and plant growth. Photosynthesis speeds up as the amount of CO2 in the air increases, as long as there is enough light to power it (to an upper limit). Photosynthesis slows to a crawl and virtually stops at a CO2 concentration of around 200 ppm. Lacking CO2, plants continue respiration and growth for a short time, until their sugars are used up; then they slow down their metabolism to conserve energy. Only when more CO2 is available can the plant processes continue.
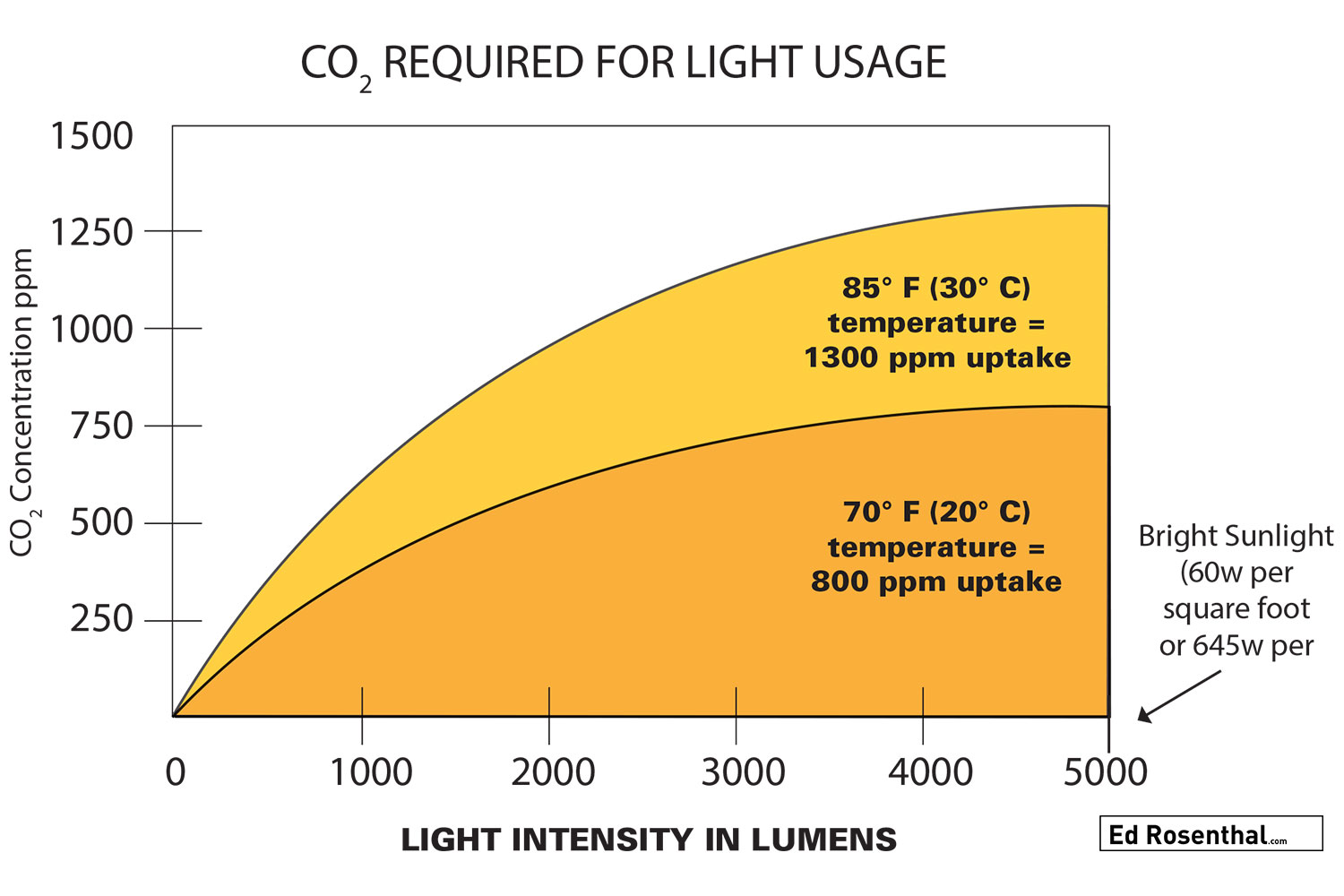
Light level, temperature and CO2 level must all increase for the plant to utilize resources most efficiently.
At less than 100 ppm of CO2 photosynthesis does not take place and plants suffer a net loss of sugar due to respiration.
At 100 ppm CO2 respiration and photosynthesis are equal so there is no net loss or gain.
At 400 ppm (same as outside air) photosynthesis increases quickly as the CO2 levels climb.
The increase in photosynthesis is more moderate as the CO2 concentration climbs to 800 ppm.
The increase is moderate, but significant between 800 and 1200 ppm.
CO2 at normal levels is not dangerous. It is a non-flammable gas. It is non-toxic at the low levels growers employ. CO2 can pose health risks in extreme concentrations (above 50,000 ppm), but this level is more than 30 times the maximum plants find useful.
What you want to know about indoor CO2 tanks and lighting
Inside a grow tent, an OG Growlite reflector is cooled using 8-inch duct work. A single Pineapple Kush plant is being super-cropped so that it covers the whole area of the tent.
When plants are growing in an enclosed area, there is a limited amount of CO2 for them to use. Under bright lights, CO2 is used up quickly. Enclosed gardens with no ventilation are also rapidly depleted to the point where the photosynthesis rate slows to a virtual stop at 200 ppm. Only when more CO2 is added to the mix does photosynthesis resume.
A closed closet or other small gardening space can be recharged with CO2 simply by opening the door or curtain to let in fresh air. This increases the CO2 content of the closet passively, as air naturally equalizes the concentrations of oxygen (O2) and CO2 inside and outside the growing space, exchanging the higher O2 levels with CO2. Adding a small fan expedites the air exchange.
The rate of photosynthesis has the greatest increase as the CO2 level climbs from 0-200.
In this garden, air is enriched as it passes through the tubes.
Under low-light conditions (150 mols or 1150 fc) (12,330 lux), the rate of photosyntheses increases as CO2 rises to 400 ppm. Increasing the CO2 concentration beyond that without increasing light intensity does not result in a higher rate of photosynthesis.
The plant cannot take advantage of higher CO2 levels until the light intensity increases.
At a light intensity of 600 mol (4600 fc) (49,310 lux), the photosynthesis rate increases more as CO2 concentration is increased to 400 ppm. The rate of increase declines a bit after that, but the photosynthesis rate continues to increase as CO2 levels reach 600 ppm.
Above 600 ppm of CO2, the photosynthesis rate continues to climb but at an even slower rate, until the rate increase levels off at about 1200 ppm.
The reflectors, with no bottom glass, draw in air as it exits through a carbon filter.
When the plants receive between 4500- 5500 fc (48,240 lux) of light, they can utilize between 1200-1300 ppm of CO2. While very few gardens are supplied with more than 7500 fc (80,400 lux) of light, at that intensity the plants can use up to 1500 ppm of CO2, the enrichment rate recommended by some manufacturers.
The easiest way to supply carbon dioxide is to use a CO2 tank kit.
The kit consists of a CO2 meter, pressure regulator, and a solenoid valve. For most gardeners, 20 or 50 pound tanks (the weight of the gas), are the most convenient. Tanks can be bought or rented.
Other options for indoor CO2
CO2 tanks are a common way to raise CO2 levels in a garden, but there are other ways:
Instead of using a tank, you can use a meter that regulates a CO2 generator that burns propane or natural gas.
You can also use metabolic and chemical processes to produce CO2, or obtain dry ice, which sheds CO2 as it evaporates.
Here’s how you can calculate how much CO2 you need
Outside of the grow tent, the air conditioner and CO2 tank are installed.
You can calculate how much CO2 is needed to bring a growing area to 1,000 ppm by multiplying the cubic area of the growing room (length x width x height) by .001. The total represents the number of square feet of gas required to reach optimum CO2 range.
For instance, a room 13’ x 18’ x 12’ contains 2808 cubic feet: 2808 x .001 equals 2.8 cubic feet of CO2 required. A room 3 x 4 x 3 meters contains 36 cubic meters and would require .036 cubic meters of CO2.
This CO2 regulator is adjustable from 0.5-15 cubic feet (0.014-0.42 cubic meters) per hour and is available from C.A.P. Controllers.
CO2 regulators attach to CO2 tanks and allow the grower to pre-set and adjust the amount of CO2 being released into the room. This CO2 regulator is adjustable from 0.5-15 cubic feet (0.014-0.42 cubic meters) per hour and is available from C.A.P. Controllers. The pressure regulator, flow rate valve and solenoid switch which opens and closes the valve are all regulated by the ppm meter.
How ever the carbon dioxide is provided, fresh air, tanked or generated, it is critical that the plants have enough to thrive.
As a large mammal, gardeners themselves are a fair source of carbon dioxide, so spending time in the garden breathing can increase supply, even more so if a friend joins.
Join our cannabis community
Follow Us